Reverse Polarity Fl Studio
Posted : admin On 09.01.2021OH!!
- What Happens With Reverse Polarity
- Electrical Outlet Reverse Polarity
- Fl Studio 12 Free Download
- Reverse Polarity Fl Studio
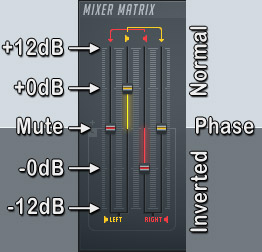
What Happens With Reverse Polarity
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube. The Send switches in FL Studio's Mixer take the audio after the Mixer Track fader, so this is known as a post-fader send. To create a pre-fader send you need to extract the audio from a point before the fader, in this case, any of the Effects slots. Usually Slot 1 is best since it won't have any preceding effects. Vypress chat. To do this use Fruity Send. Open the MIDI Control Center 2. Press on the 'sync' bouton 3. Click on the Sustain pedal input 4. In the 'Selected Control Parameters' section, set the Min to 127 and Max to 0.
sorry
Inverse Polarity is what you said.. doesn't matter

does this help:
inverse polarity' in the sense that you're describing is known as 'Differential transmission' and simply means that you have two wires with opposite voltages on them - i.e. when one wire has a high voltage, the second has a low volatage, and vice-versa. The technical answer is phrased a bit differently - rather than referring to a high and a low voltage, what you're really measuring is the voltage difference between the two wires. Imagine hooking a voltmeter between the two wires - a '1' may be transmitted by having a positive voltage appear on the voltmeter; a '0' may be transmitted by having a negative voltage appear on the voltmeter. It's really no harder than this.
The reason is relatively simple - every wire in the universe is also an antenna, and picks up stray signals. You can imagine that this can be a huge problem when you imagine running a 100 meter length of twisted-pair ethernet cable. That's one big antenna. So, how do you eliminate the stray signals?
You start off by twisting the wires together. If you open up any modern communications cable (USB, Ethernet, Firewire, etc) you'll notice that the data wires are twisted around each other. Because of this twisting and the consequent extremely close coupling between the wires, almost all of the stray signals picked up by one wire are also picked up by the other one. So, now you have two noisy signals rather than one - doesn't seem like we've gotten anywhere, ehh?
Well, now we do some mathematics. Imagine the signal in one wire is (S+N), where S is the original signal, and N is the noise it's picked up. The signal in the second wire will then be (-S + N), where the signal is exactly the opposite of the first wire, but the noise is the same (it didn't get inverted). What happens when you subtract the second signal from the first?
Result = (S+N) - (-S + N)
Result = S + N + S -N
Result = 2S Izotope ozone 6 free mac.
What happened? We ended up with twice the amplitude of the first signal, and all of the noise got cancelled out!
As to how you generate a signal, it's pretty easy. In order to transmit a signal down a cable, you normally run it through an amplifier inside whatever electronics it starts from. Note that in this sense, the 'amplifier' is a tiny circuit, not a big black box with a dial that goes from 0 to 11, though the big black box probably has a bunch of the tiny amplifiers.
Electrical Outlet Reverse Polarity
Fl Studio 12 Free Download
Anyway, in order to generate this differential signal, you run it through two seperate amplifiers - one an Inverting amplifier (google it, or simply accept that this exists), one a non-inverting amplifier. Presto, the two outputs are attached to a wire, and you have a differential signal.
Reverse Polarity Fl Studio
I didn't write that BTW